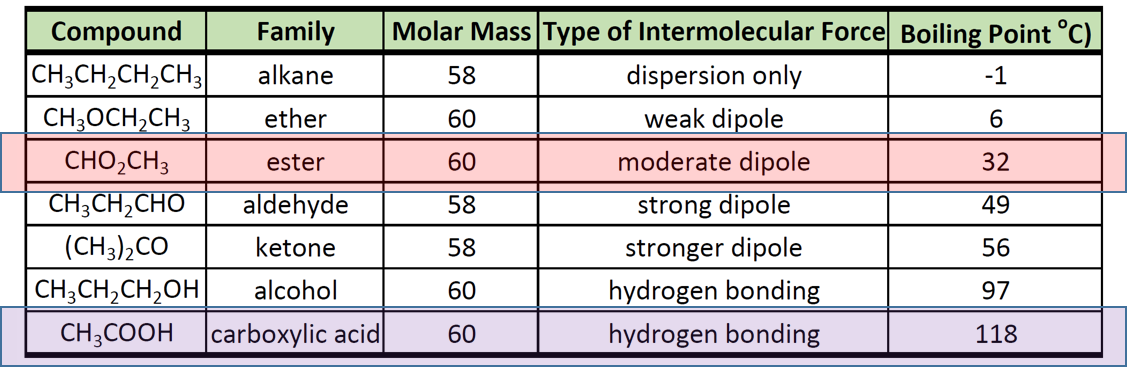
Boiling Point of Ester and Carboxylic Acid
Salts and esters of valeric acid are known. Synthetic lubricants can be manufactured using chemically modified petroleum components rather than whole crude oil but can also be synthesized from other raw materialsThe base material however is still overwhelmingly crude oil that is distilled and then modified physically and chemically.

Physical Properties Of Carboxylic Acids Youtube
The boiling range is generally 160360C 320680F.
. Since 2010 diesel fuel may contain up to 7 vol fatty acid methyl ester FAME in Europe to meet biofuels. Acid Dyes Azoic Dyes Basic Dyes Direct Dyes Disperse Dyes Dye Intermediates Mordant Dyes Oil Dyes Other Stains and Dyes Synthetic Reagents Acids and. In general dicarboxylic acids show similar chemical behavior and reactivity to monocarboxylic acidsDicarboxylic acids are also used in the preparation of.
1-Butanol bp 1175C 2-Butanol bp 935C 2-Methyl-2-propanol bp 322C. Valeric acid or pentanoic acid is a straight-chain alkyl carboxylic acid with the chemical formula CH 3 CH 2 3 COOHLike other low-molecular-weight carboxylic acids it has an unpleasant odorIt is found in the perennial flowering plant Valeriana officinalis from which it gets its nameIts primary use is in the synthesis of its esters. The carboxyl COOH group is so-named because of the carbonyl group CO and hydroxyl group.
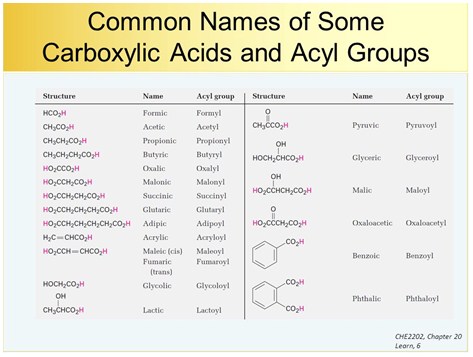
Chapter 5 Carboxylic Acids and Esters 17 Common Name Structural Formula BP C MP C Solubility g100 mL H2O Formic acid HCO2H 101 8 Infinite Acetic acid CH3CO2H 118 17 Infinite Propionic acid CH3CH2CO2H 141 -21 Infinite Butyric acid CH3CH22CO2H 164 -5 Infinite Valeric acid CH 3CH23CO2H 186 -34 5 Caproic acid CH3CH24CO2H 205 -3 1. As with carboxylic acids two phosphoric acid molecules may combine with the loss of water to form a di phosphate ester also referred to as pyrophosphate. Synthetic oil is a lubricant consisting of chemical compounds that are artificially made.
Hydrolysis of ester gives carboxylic acid and. Carboxylic acid any of a class of organic compounds in which a carbon C atom is bonded to an oxygen O atom by a double bond and to a hydroxyl group OH by a single bond. The following data for isomeric four-carbon alcohols show that there is a decrease in boiling point with increasing substitution of the OH-bearing carbon.
The general molecular formula for dicarboxylic acids can be written as HO 2 CRCO 2 H where R can be aliphatic or aromatic. 3551C at 760 mmHg. However as phosphoric acid has further -OH functionalities triphosphates may also be formed.
Carboxylic acids and carboxylates prevent free water in the gasoline from rusting or corroding. Materials Organic ligands for MOF materials Carboxylic MOF ligands Halogen series MOF ligands of nitrogenous. How might you account for this trend.
A fourth bond links the carbon atom to a hydrogen H atom or to some other univalent combining group. Linear Structure Formula -InChI Key. A dicarboxylic acid is an organic compound containing two carboxyl functional groups COOH.
2 is similar in composition to fuel oil no.
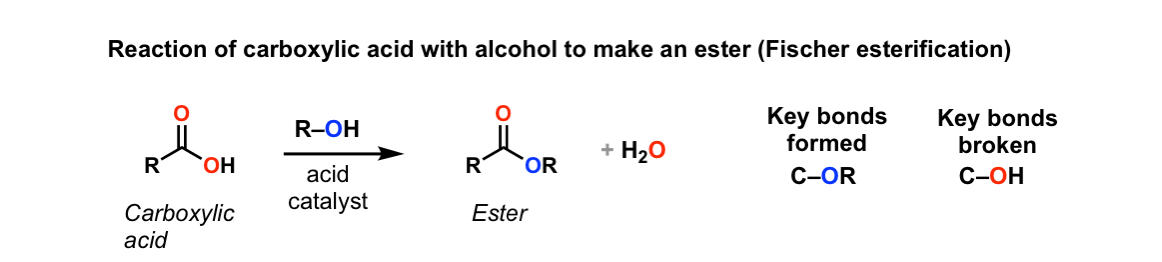
Conversion Of Carboxylic Acids To Esters Using Acid And Alcohols Fischer Esterification Master Organic Chemistry

Carboxylic Acids And Esters A Level Chemistry Revision Notes

No comments for "Boiling Point of Ester and Carboxylic Acid"
Post a Comment